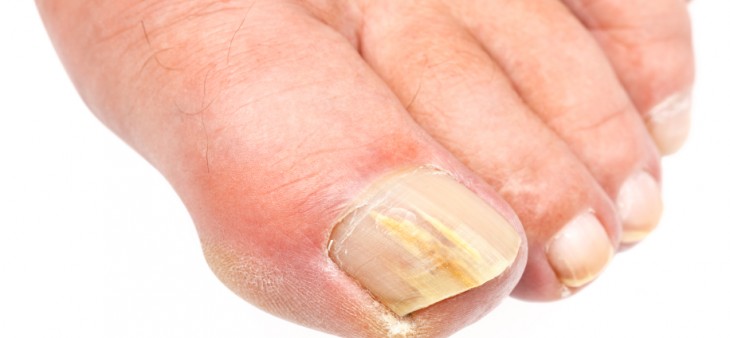
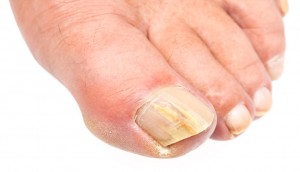
 A fungal nail infection referred to in medical terms as onychomycosis, occurs when fungi, a kind of microorganism infect your nails. You may first notice the infection as a white or yellow spot under the tip of your nail. Symptoms of a fungal infection may include brittleness, discoloration, thickening and crumbling of the nail, as well as debris under the nail itself. In some cases, the nail can detach from the nail bed.
A fungal nail infection referred to in medical terms as onychomycosis, occurs when fungi, a kind of microorganism infect your nails. You may first notice the infection as a white or yellow spot under the tip of your nail. Symptoms of a fungal infection may include brittleness, discoloration, thickening and crumbling of the nail, as well as debris under the nail itself. In some cases, the nail can detach from the nail bed.
Approximately 50 percent of all nail disorders are fungal infections.
Factors that may lead to developing a fungal nail infection include:
[su_list_fav]- Trauma that allows the pathogen to enter the nail or nail bed
- Abnormal PH level of the skin
- Overexposure to water or detergents
- Not drying off the feet thoroughly after bathing or exercise
- Wearing tight, or enclosed shoes that do not allow feet to breath.
- Diabetics and the elderly have an increased risk of contracting a toenail fungus because their immune system is compromised. For this reason, it is often recommended that they should have their nails cut and callus debrided by a podiatrist.
A Podiatrist will implement a comprehensive assessment plan to ensure that the treatment really gets to the cause of the problem.
This may include:
[su_list_fav]- An initial assessment to determine if there is a fungal nail infection present
- A review of the cause of the infection
- A treatment plan outlining the most appropriate management
- Measures to ensure that once the infection is eradicated that the chances for re-infection are minimised
Treatment
Treatment of a fungal nail infection can take a while to complete, and is best begun at the early stages of infection before it has spread deeper into the nail. See your Podiatrist right away if you see any change in your nail or feel swelling or pain. Fungal infections used to be difficult to treat, but new therapies can often permanently heal your nails.
Your Podiatrist will choose the best treatment for you based on the type of infection and the amount of the nail involved. Treatment can range from 3 to 18 months to completely clear up the fungal infection.
Laser treatment: This is a major advancement in the treatment of fungal nail infections with over 80% success rate. The laser light is used to penetrate the skin and nail plate to destroy the fungus in a single treatment without damaging the nail or skin itself. The procedure is pain-free and there are no side effects. After the treatment, the nail will grow out free of fungal infection. Cost is to be considered although for persistent cases it is cost effective. This treatment is only offered by leading providers at this stage.
Topical medication: A medicated nail lacquer is applied to the nails daily for a long period. There are no side effects, although you must take care to avoid application to the adjacent skin as this can cause irritation. Application of topical agents is quite a laborious task and there are generally compliance factors to consider.
Oral medication: A medication is taken orally generally for 6-12 weeks. To have these medications covered under the pharmaceutical benefits scheme a microscopy study of your nail cuttings is required to confirm that a yeast infection is present. In addition, before treatment, the risk of adverse effects such as liver disease needs to be evaluated. The success rate is approximately 50%, however, side effects are well documented in some people who take these oral antifungal medications and an excessive cost is to be considered with newer oral antifungals.
If you suspect you have developed a fungal toenail infection it is advised that you see your podiatrist who can professionally diagnose and treat the condition.
